Endometrial cancer, a type of cancer that begins in the lining of the uterus, is one of the most common cancers affecting women. Understanding the risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options is crucial for early detection and better outcomes. In this article, we will explore seven essential insights about endometrial cancer.
What is Endometrial Cancer?
Definition and Types
Endometrial cancer originates in the endometrium, the inner lining of the uterus. It primarily affects postmenopausal women but can occur at any age. There are two main types of this cancer:
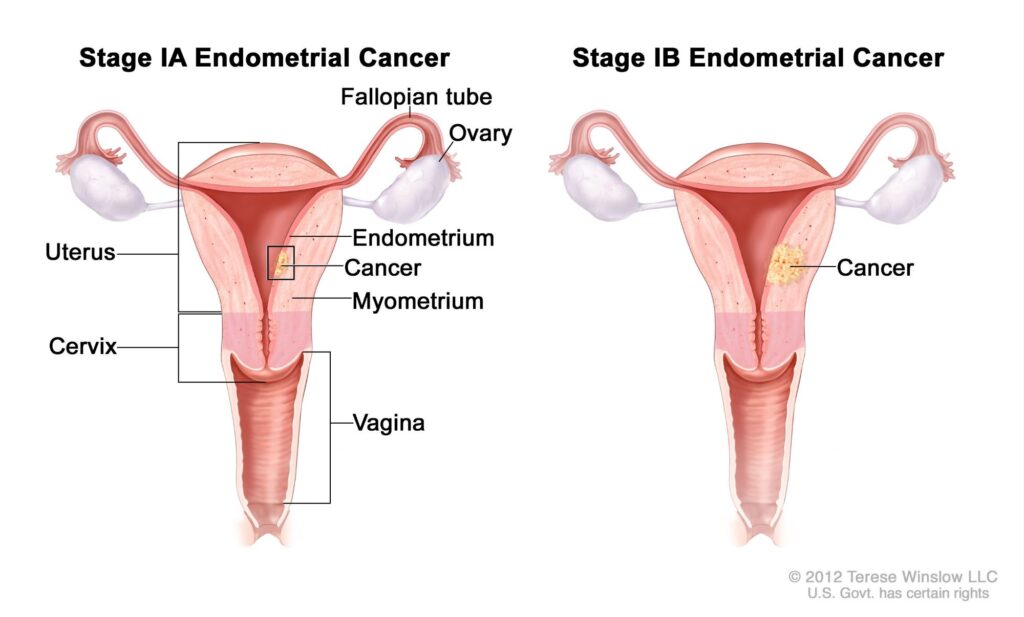
1. Type I: The most common form, typically estrogen-dependent and usually diagnosed at an early stage.
2. Type II: Less common, more aggressive, and not associated with estrogen.
Prevalence
Endometrial cancer is the fourth most common cancer among women in the United States. According to statistics from the American Cancer Society, it is estimated that approximately 66,000 new cases will be diagnosed each year.
Risk Factors for Endometrial Cancer
Hormonal Factors
Hormonal imbalances play a significant role in the development of this cancer. Conditions that increase estrogen levels without sufficient progesterone can heighten risk. This includes:
– Obesity: Excess body fat can lead to higher estrogen production.
– Menstrual Irregularities: Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can disrupt hormonal balance.
Genetic Factors
Family history and genetic predispositions can also influence the risk of this cancer. Women with hereditary conditions such as Lynch syndrome (hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer) are at an increased risk.
Other Risk Factors
Additional risk factors include:
– Age: Most cases occur in women over 50.
– Diabetes: Women with diabetes are more likely to develop this disease.
– Tamoxifen Use: While used to treat breast cancer, tamoxifen can increase the risk of endometrial cancer.
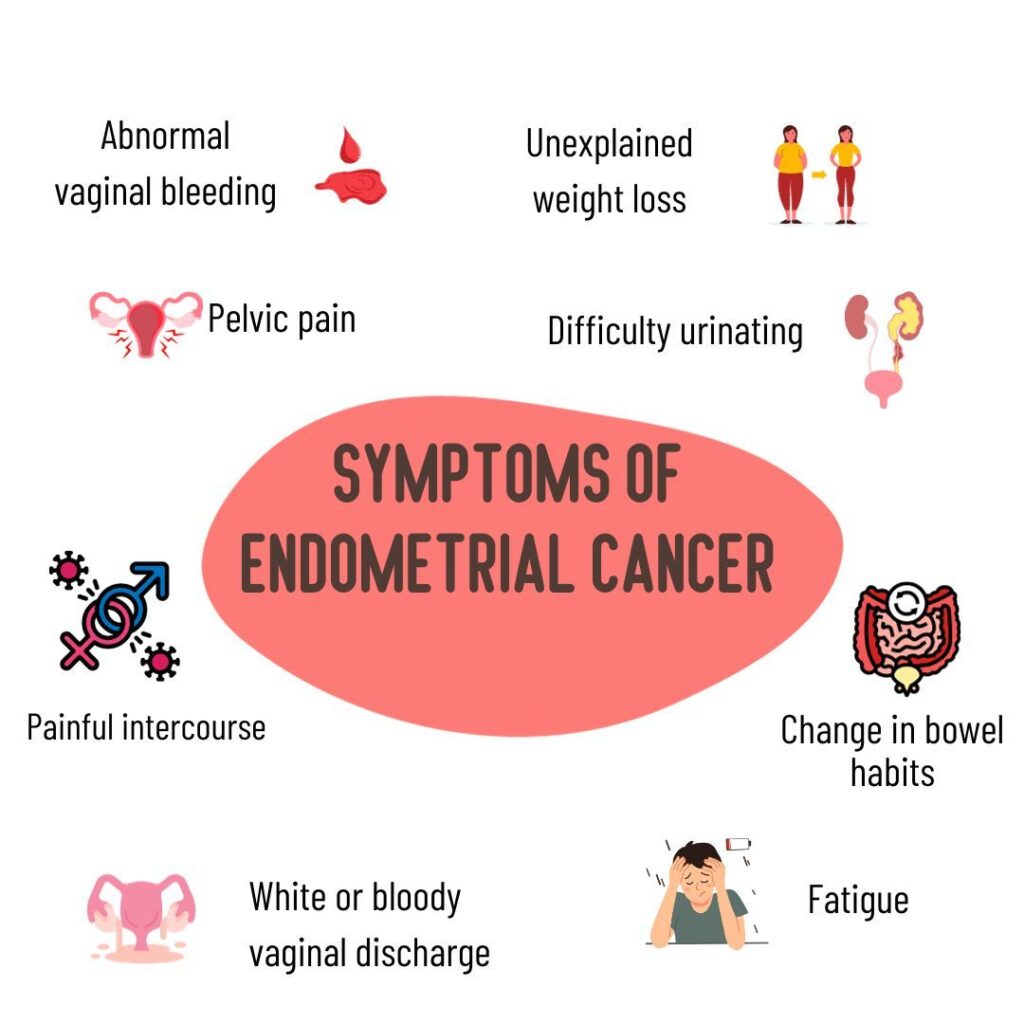
Symptoms of Endometrial Cancer
Common Symptoms
Early detection is critical for successful treatment, and recognizing symptoms is vital. Common signs of this cancer include:
– Abnormal Vaginal Bleeding: This can include bleeding between periods or heavy bleeding during menstruation.
– Postmenopausal Bleeding: Any bleeding after menopause should be evaluated promptly.
– Pelvic Pain: Persistent pain or discomfort in the pelvic area can be a sign of this disease.
Other Symptoms
In addition to the primary symptoms, women may experience:
– Unexplained Weight Loss: Sudden weight loss without dieting could indicate an underlying issue.
– Changes in Urination: Increased frequency or pain during urination can occur if the cancer spreads.
Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer
Initial Evaluation
If endometrial cancer is suspected, a healthcare provider will conduct a thorough evaluation, which may include:
– Medical History: Discussing symptoms, menstrual history, and risk factors.
– Pelvic Exam: A physical examination to check for abnormalities.
Diagnostic Tests
Several tests may be performed to confirm a diagnosis:
1. Transvaginal Ultrasound: This imaging technique helps visualize the uterus and measure the endometrial thickness.
2. Endometrial Biopsy: A small sample of the endometrial tissue is taken to check for cancerous cells.
3. D&C (Dilation and Curettage): If a biopsy is inconclusive, a D&C may be performed to gather more tissue for analysis.
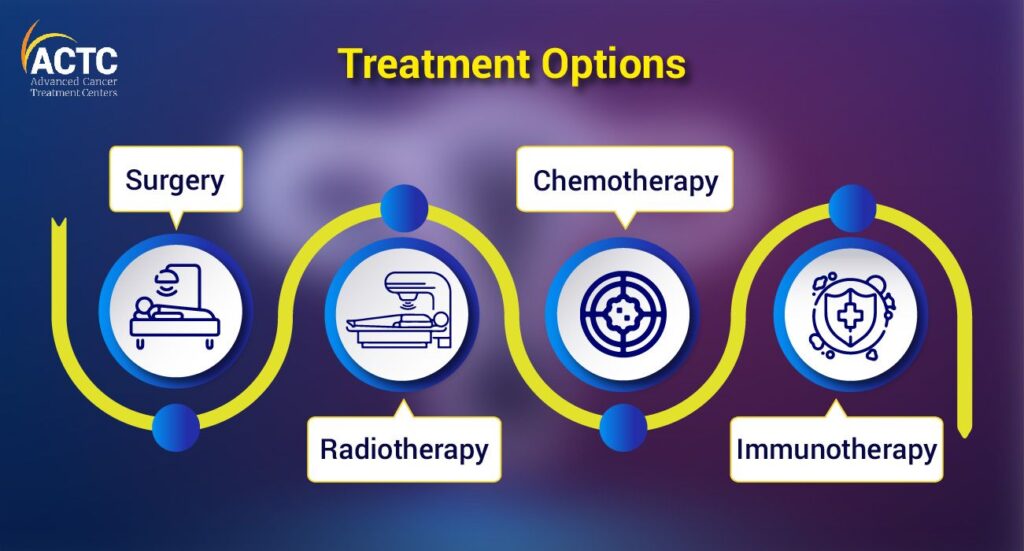
Treatment Options for Endometrial Cancer
Surgery
Surgery is often the first line of treatment for endometrial cancer. The primary procedure is a hysterectomy, which involves the removal of the uterus and may include:
– Salpingo-Oophorectomy: Removal of the ovaries and fallopian tubes.
– Lymphadenectomy: Removal of nearby lymph nodes to check for cancer spread.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy may be recommended after surgery to eliminate any remaining cancer cells. It can also be used as a primary treatment for patients who are not surgical candidates.
Chemotherapy
For advanced or aggressive types of endometrial cancer, chemotherapy may be necessary. This treatment uses drugs to kill cancer cells and is often combined with other therapies.
Hormonal Therapy
In cases of hormone-sensitive endometrial cancer, hormonal therapy may be used to slow growth. Medications that lower estrogen levels or block its effects can be effective.
Living with Endometrial Cancer
Follow-Up Care
Post-treatment, regular follow-up care is essential to monitor for recurrence. This typically includes:
– Physical Exams: Regular check-ups to assess health and any new symptoms.
– Imaging Tests: Periodic imaging may be necessary to ensure the cancer has not returned.
Emotional Support
Navigating a cancer diagnosis can be emotionally challenging. Seeking support from counselors, support groups, or online communities can provide comfort and information.
Lifestyle Changes
Making healthy lifestyle changes can positively impact overall well-being and may help reduce the risk of recurrence. These include:
– Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can support recovery.
– Regular Exercise: Physical activity can improve mood and overall health.
– Stress Management: Techniques such as yoga, meditation, or mindfulness can help manage stress levels.
Takeaway
Endometrial cancer is a significant health concern for women, but understanding risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options can lead to early detection and better outcomes. With advancements in research and treatment, many women can effectively manage this disease and lead fulfilling lives. Awareness and education are key in empowering women to take control of their health, seek timely medical advice, and promote a proactive approach to wellness.