The CFO & Future of Finance Summit 2024, hosted at the elegant Labadi Beach Hotel, was a grand event celebrating leadership and innovation in finance. Among the luminaries of the financial world, one name stood out—Roberta Awinmah Ayalingo, Wibexly’s distinguished Financial Consultant, who received a prestigious award recognizing her exemplary contributions to the sector.
A Recognition of Impact
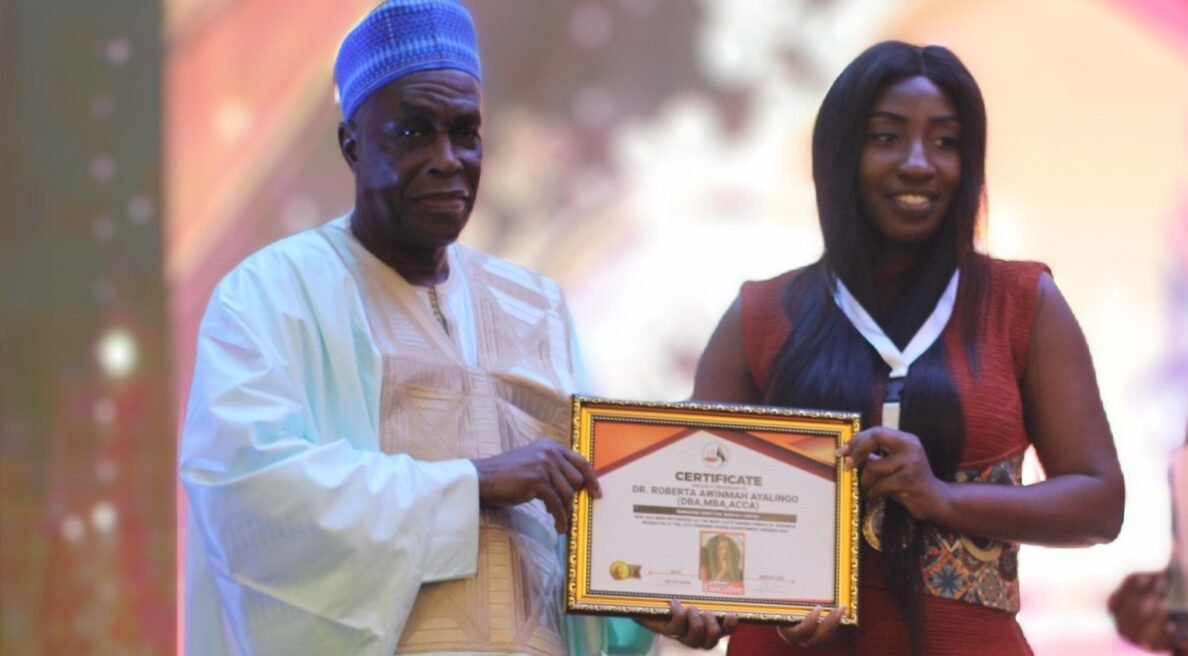
Roberta’s accolade is a testament to her remarkable career. At Wibexly, she is celebrated not only for her sharp financial strategies but also for her passion for delivering solutions that drive growth. Her recognition at this summit reflects her pivotal role in transforming financial operations and fostering a culture of excellence within and beyond her organization.
Networking with Industry Titans
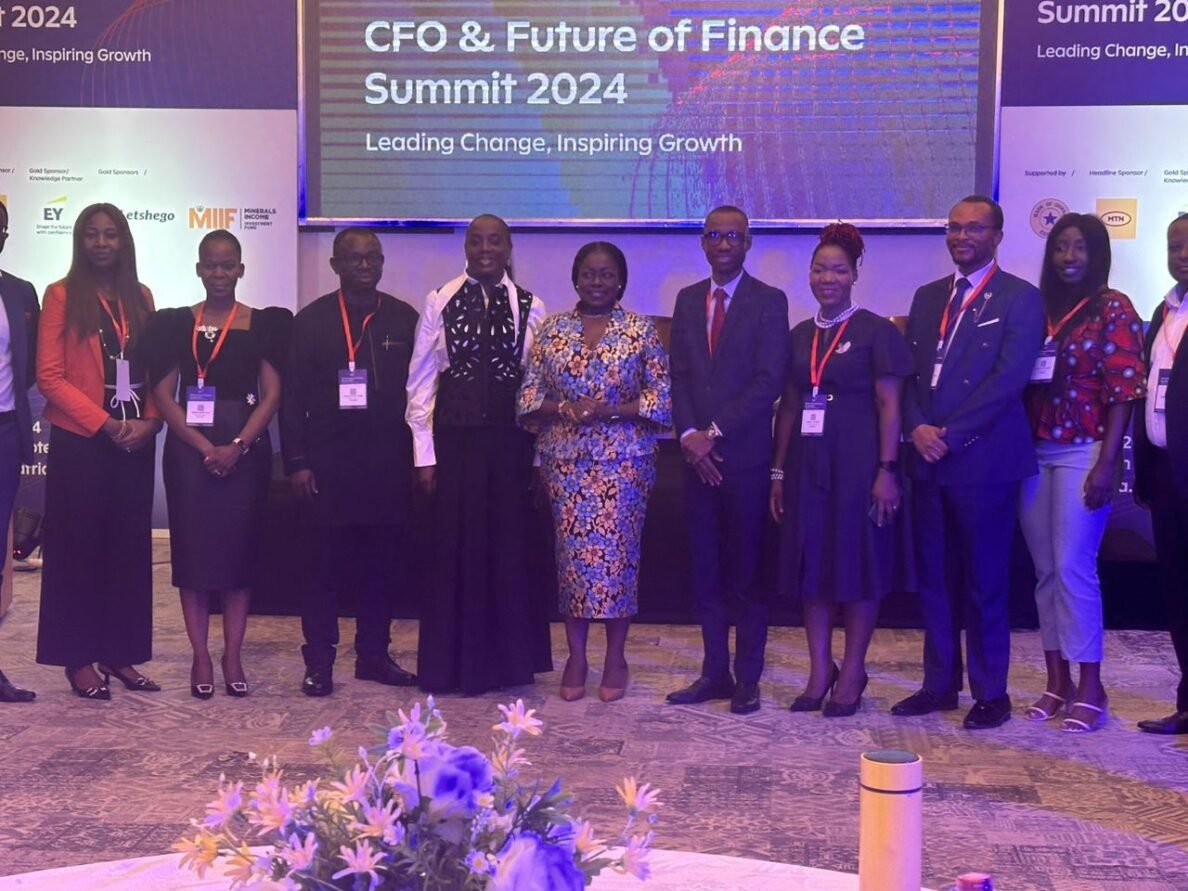

The summit provided a rare opportunity for attendees to connect and exchange ideas. Roberta engaged with some of the most influential figures in finance, including:
- Antoinette Kwoffe, CFO & Board Director, MTN Ghana
- Poelo Mkpayah, Group CFO, Letshego West Africa
These interactions highlighted the event’s mission to inspire growth through collaboration, paving the way for future partnerships and innovative financial solutions.
The Summit: A Hub of Inspiration
Organized under the theme “Leading Change, Inspiring Growth”, the CFO & Future of Finance Summit brought together trailblazers, policy makers, and thought leaders. Attendees delved into critical topics shaping the future of finance, such as technological innovations, sustainable finance practices, and leadership in a dynamic economic landscape.
The summit’s vibrant panels and interactive sessions empowered participants to rethink strategies and position their organizations for success. For Roberta, this was not only an acknowledgment of her hard work but also an opportunity to learn and contribute to the discourse shaping the finance industry’s future.
Looking Ahead
Wibexly takes immense pride in Roberta’s achievement. Her dedication to excellence and innovation continues to set benchmarks for the company and the broader financial community. As Roberta builds on this milestone, her work will undoubtedly lead to transformative impacts, championing the future of finance.
Join us in celebrating Roberta Awinmah Ayalingo’s incredible journey! Her story is a powerful reminder of what’s possible when talent meets opportunity, and when innovation is driven by a passion for positive change.
Stay tuned as we continue to share more updates and stories of excellence from the finance world.
Also Read: ‘Our priorities are wrong in Ghana’ – UG Sports Director on sports development

